Google Search Console (GSC) can seem vast and complicated if you aren’t familiar with it. However, learning how to use Google Search Console isn’t as hard as it might appear.
We suggest you invest 10-15 minutes reading this Google Search Console tutorial (or watching the video below) and another 10-15 minutes exploring the platform itself. Not only will you learn how to use Google Search Console, but you’ll also be able to quickly start gaining valuable insights that can drastically improve your website’s ability to rank in the search results.
Here is where this tutorial will take you today:
Watch the Video
What Does Google Search Console Do?
Here’s what Google has to say about what GSC can do: “Google Search Console is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site's presence in Google Search results.”
We appreciate Google’s modesty in the statement above because Google Search Console is the most powerful FREE tool available to anyone who owns a website. Even SEO professionals with expensive subscriptions to data-rich SEO platforms still turn to Google Search Console on a regular basis to advance their SEO strategies.
In our eyes, Google Search Console also allows you to:
- Establish a direct connection between your website and Google.
- Monitor the way your site is appearing and performing (ranking) in the search results.
- Identify what’s helping or hurting your site’s performance.
- Spot opportunities for improvement.
- Update Google when you make changes to your site.
- Diagnose and fix certain website issues as they arise.
The following will shine some more light on the capabilities of Google Search Console.
Verifying Ownership of a Website with Google Search Console
Verifying a website with Google Search Console achieves three aims.
- It shows Google that you own and/or manage your site.
- It establishes a formal connection between your website and Google.
- It gets you access to Google Search Console’s tools and reports.
Quick Tip: Using the same Google account (email address) to manage both Google Analytics and Google Search Console makes verification far easier.
There are a couple of different types of verification that will prove to Google that you own/manage your site:
- Domain verification.
- URL prefix verification.
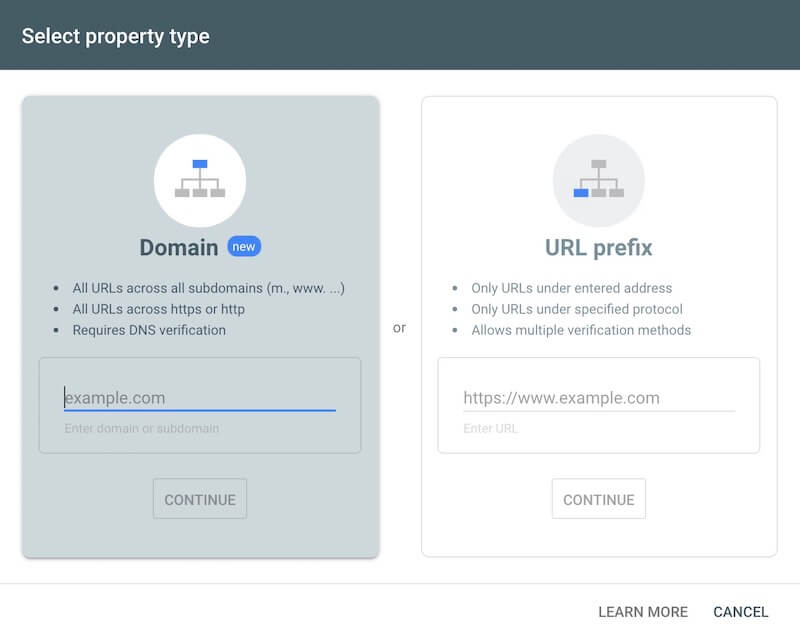
If you have only one canonical (definitive) version of your site, you can verify using a URL prefix. Just make sure to use the full URL. That is, if your homepage lives at https://www.example.com/, make sure that the URL you verify includes the full prefix (https://www) and the trailing slash (.com/) — paste it exactly as it appears in the browser above your homepage.
The cleanest way to verify a site with subdomains or multiple protocols is by using the domain verification option. It’s slightly more time-consuming and complicated than verifying via a URL prefix, and you will need access to your DNS records.
If you use the URL Prefix option and you have already connected your site to Google Analytics, your ownership may be automatically verified by Google Search Console.
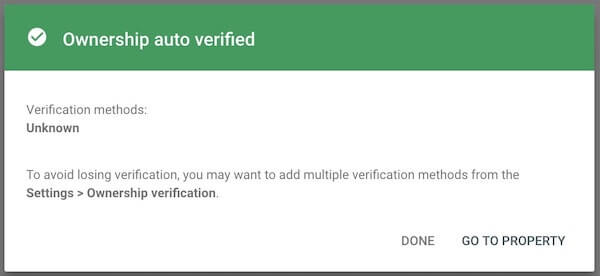
If your ownership is not automatically verified, you have several other options to complete your verification.
Depending on how your site is set up, one of these options may be better than the others. More often than not, using the HTML tag is the easiest method.
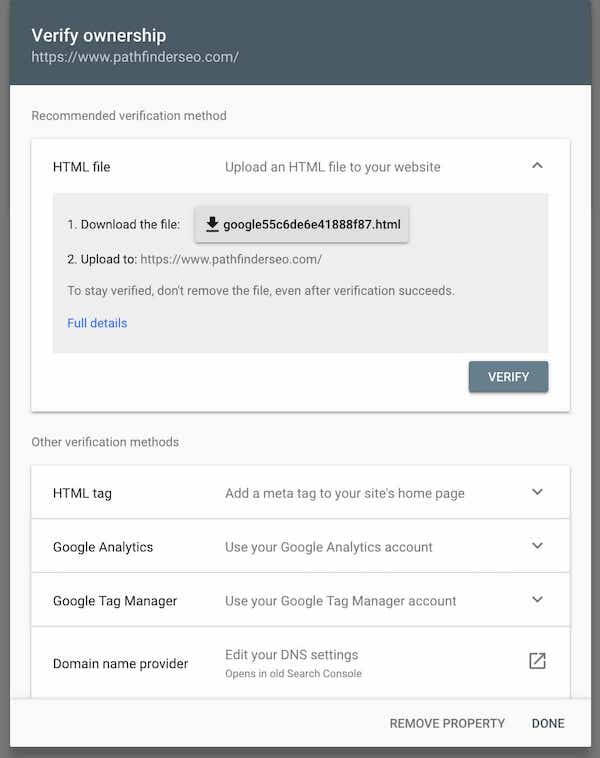
If you are a WordPress user, most popular SEO plugins like Yoast and All In One SEO Pack already have a field in their “webmaster” sections where you can easily place your HTML tag to complete verification. Click on the links above for further information on how to verify your site using those plugins.
Squarespace, Wix, Shopify, Weebly, and other CMSs each have a different process for site ownership verification.
Once you have properly verified your site, you should receive a success message. You will then be redirected to your Google Search Console Overview page.
If you are verifying your site for the first time, it might take Google a few days to crawl and index it. In the meantime, GSC won’t display detailed site information. Wait for your site to get fully indexed and for Google Search Console data to populate before continuing this tutorial.
Overview
The Overview page will appear every time you log in to Google Search Console once you’ve successfully verified your ownership of a Google Property (your website),

This Overview provides a snapshot of how well your site is doing in three of the GSC’s most important reports:
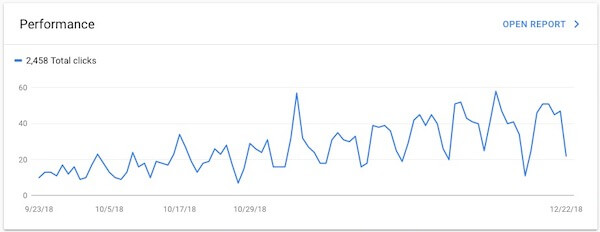
Performance
The Performance chart will show you how many people are clicking to your site from the organic search result listings. This includes regular web results, images, and videos.
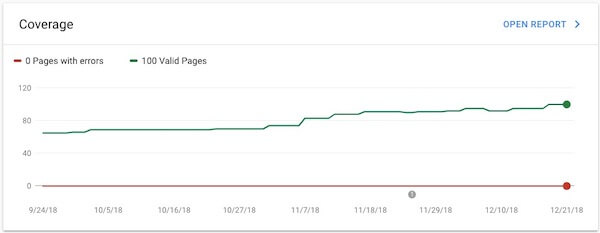
Coverage
The Coverage chart will tell you how many of the pages on your site Google has crawled and added to its index.
Enhancements
You will also see information about Enhancements you may have added to your site. What you see in this report depends on which enhancements have been added to your site.
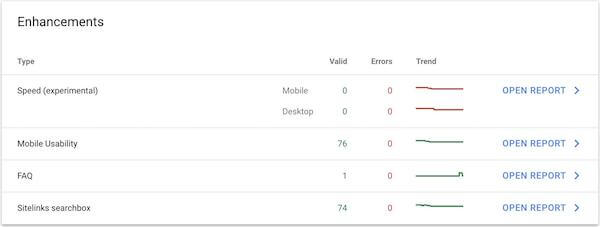
Click OPEN REPORT on any of the displayed line items to open the corresponding report in GSC.
Menu
The Overview page is the first place you’ll notice the menu — the left-hand navigation listing all available tools and reports. If you don’t see this navigation, click on the hamburger menu next to “Google Search Console” in the top left corner, and it will appear.
Not everyone’s menu looks the same; Google provides some properties with more options than others.
Now that you understand what you’ll see when you first log in, let’s dig into some of the most important reports you’ll want to use.
Using the Performance Report in Google Search Console
The Performance report is arguably the most valuable tool in all of Google Search Console. Here’s how you can learn to leverage the valuable data it provides.
For some users, the Performance report in Google will be broken up into two sections:
Search Results — Reports on your site’s performance in traditional Google Search results.
Discover — Reports on your site’s performance in Google Discover, a scrollable browsing experience customized for users of Google’s mobile app.
If your Performance report is not broken into two, it will only display data related to traditional Google Search results.
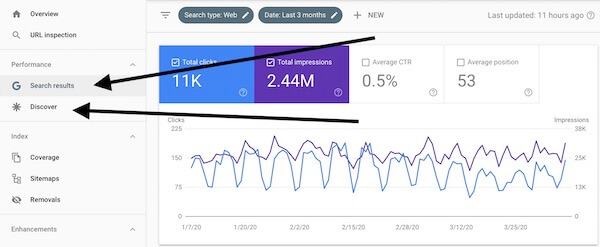
In this intro, we are only focusing on the Search results section of the Performance report because that’s the data everyone will have access to.
Performance Report Filters Bar
Start by getting to know the filters in Google Search Console. Filters allow you to sort and display your data based on the parameters that are most important to you.
By default, you will see Search type: and Date: displayed in the filters bar. You can add others by selecting the + NEW dropdown.
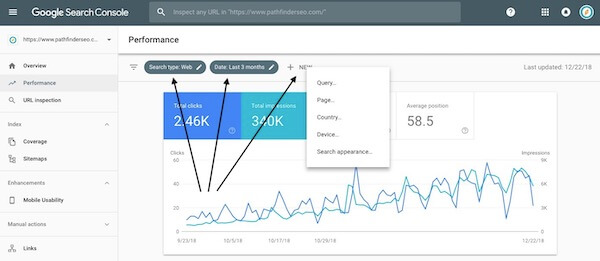
Search Type — Allows you to filter based on image, web, or video searches. It’s set to “video” by default.
Date — Allows you to set the date range, going back as far as sixteen months. The default range is “three months.” Twelve months is the most useful time frame in most cases.
+New — Allows you to add the Performance report’s various dimensions as additional filters.
Three Need-to-Know Filters
Individual Page — By using the + New > Page filter with Exact URL and then typing in any URL on your site, you can see how that particular URL is performing in search results, which keywords (queries) it’s ranking for, and much more.
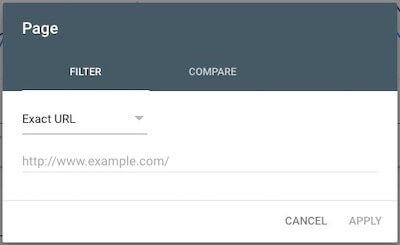
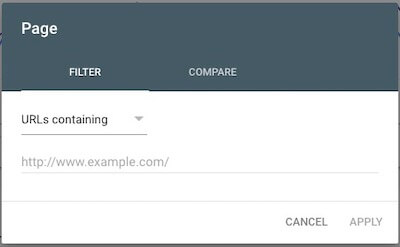
Content Type — By using the + New > Page filter with URLs containing and then typing in a slug like /blog/ or /product/, you can see how pages in a particular category are doing. This can be great if you want to evaluate the performance of all your blog posts, product pages, etc., separate from all your other pages.
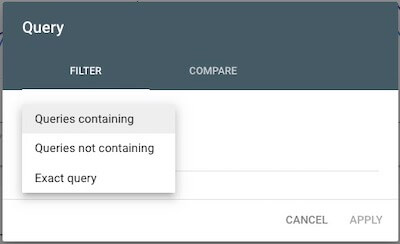
Keywords — Using the + New > Query filter with Queries containing or Exact query and then typing in a keyword will let you see how well your pages are performing for the specific keywords and keyphrases most important to your business.
Once you have your filters set, you’ll see your metrics displayed in a graph below your filters:
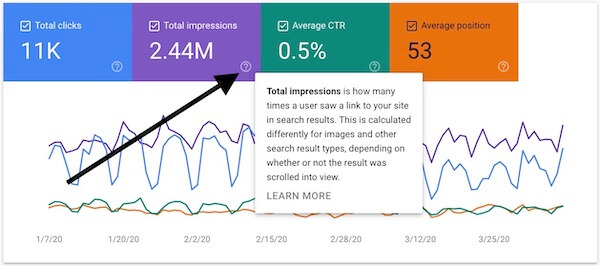
Performance Report Metrics Chart
Metrics are the quantitative measurements of your site’s performance in Google Search. There are four key metrics in the Performance report:
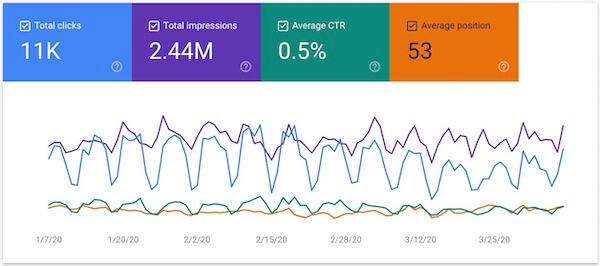
Total Clicks — Tells you how many people are clicking through to your site when they see your pages listed in the search results.
Total Impressions — Shows how often pages on your site are appearing as listings in the search results.
Average CTR (click-through rate) — The average percentage of people who see your pages in the search results and then decide to click on one.
Average Position — The average position/rank for your page when they appear in Google Search results.
If you want any one of those four metrics graphed, simply click on the corresponding tab to highlight it. If you want a metric removed from the graph, just click the tab again.
If you want more information about any one of those metrics, click on the little question mark icon, and Google will provide additional information.
Once you’ve looked through the metrics chart, you can scroll down to the dimensions table.
Performance Report Dimensions Table
The dimensions table displays the various measurable attributes of your site’s search performance across the top.
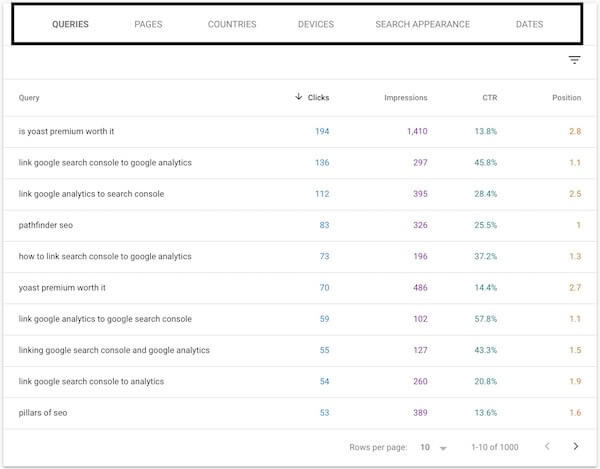
You can analyze each dimension using the four key metrics: Total Clicks, Impressions, Click-Through Rate (CTR), and Average Position. If a metric isn’t displaying in the table, make sure it is highlighted above in the metrics chart.
Here’s the data you can access by clicking on each dimension:
Queries — Shows the search terms (keywords or key phrases) that trigger your site to appear in the search results.
Pages — Shows how individual pages on your site are performing in the search results.
Countries — Compiles search metrics based on the country in which searches are conducted.
Devices — Shows metrics based on the specific devices being used to conduct searches.
Search Appearance - Allows you to see data for special categories of search results such as AMP, Job Listings, Media Actions, etc.
Dates - Displays metrics based on individual days of the year.
If you want to further refine the information displayed in this table, you can use any of the filters above to add parameters. This is especially helpful if you want to see information for a single page, keyword, particular date range, etc.
Using The Performance Report to Drive More Traffic & Business
We recommend you experiment with this report to see what kinds of insights you can gather. As a fun exercise, try to answer some of these questions:
- What are the top performing keywords on each important page of your site? Are you correctly optimizing those important pages around those keywords?
- Which queries are returning the highest click-through rates (CTRs)? Does your content provide more useful information to answer those queries than other sites on the internet?
- Which important pages on your site are driving little to no organic traffic? What can you do to improve and optimize them?
- Which pages received the most clicks over the last six months? Are you making it easy for people to convert on these pages?
- Which pages on your site are showing up frequently in search results (Impressions) without receiving clicks? Can you improve your title tags and meta descriptions to improve your click-through rate?
- Which of your pages are on the cusp of breaking into the first page, i.e. average position lower than ten? How can you improve the content on those pages and their on-site optimization?
Answering each of these questions can help you make sense of your site’s performance in the search results and help you start thinking about strategies that will help your site rank better in the future.
If you want to gain a better understanding of your Performance data, check out Google’s documentation.
Indexation Reports
There are three key indexation reports/tools that Google gives you access to in GSC. Let’s take a look at how to use each one starting with the URL inspection tool.
Using the URL Inspection Tool
If you are ever wondering “Is this page appearing on Google?”, there’s a simple way to find out: the URL inspection tool.
Click on “URL inspection” and/or simply type the URL into the search bar at the top of GSC, then hit return.

You will be able to find out if that page:
- Is/isn’t on Google.
- Has/hasn’t been submitted for Google to index via your sitemap.
- Is/isn’t mobile-friendly.
- Is/isn’t eligible for any enhancements.
If the page you just inspected is not already in Google's index (which means it's not yet appearing in the search results), click REQUEST INDEXING. This will trigger Google to crawl and index that individual page so that it can start showing up in the search results.
This is a great tool to use on an as-needed basis. However, using it to request indexing for every page on your site is not inefficient, which is why Google supplies us with the Sitemaps tool.
Using the Sitemaps Tool
An XML sitemap is a list of all the URLs that are available to appear in the search results. The best way to get this list of pages into Google Search is by submitting your XML sitemap via the Sitemaps tool in Google Search Console.

Before you submit your sitemap to Search Console, make sure it doesn’t contain any URLs with thin or duplicate content.
Then, copy the entire URL of your XML sitemap (typically https://examplesite.com/sitemap.xml or https://examplesite.com/sitemap_index.xml) and paste that complete URL into the Sitemaps tool in GSC. Click SUBMIT.
This will trigger Google to immediately crawl your sitemap and make sure you’re not missing any of the pages that you want to appear in the search results.
You’ll want to resubmit your XML sitemap (using this tool) any time you create new content or make changes to your site that Google should know about.
Once you’ve submitted all your URLs to Google, the Coverage Report will show you how your site is being indexed. That is, which pages are and are not appearing in Google search results, and why.
Using the Coverage Report
Coverage is short for “Index Coverage” Report. This report shows you which pages Google has either crawled and indexed, or attempted to crawl and index.
It categorizes pages into four main categories based on indexation status.
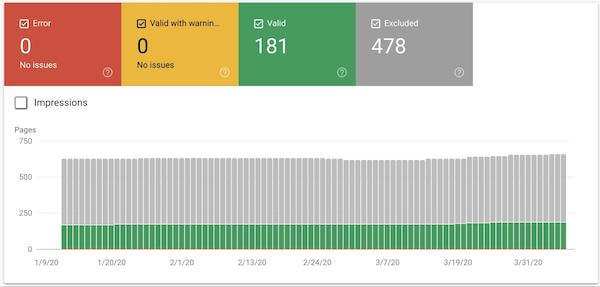
Error — Shows pages that aren’t showing up in the search results because Google is having issues indexing them.
Necessary Actions: Google will tell you the specific issue for each page marked with “Error.” Address each error using either Google’s documentation or guidance from elsewhere on the internet.
Valid with warnings — Google isn’t really sure if you want these pages shown in the search results, but is showing them anyway.
Necessary Actions: Identify why Google is taking issue with these pages and address the issues using the suggestions in Google’s documentation.
Valid — Displays pages Google has indexed and is actively displaying in search results.
Necessary Actions: Make sure the quantity of pages is relatively flat over time. Noticeable spikes or drops may indicate issues. Also, make sure this list does not contain any pages you do not want to appear in search results. If it does, add no-index tags to each page you want excluded from the search results.
Excluded — Shows pages that are not indexed — either because you told Google not to index them, or because Google thinks they shouldn’t be indexed. These pages will not appear in the search results.
Necessary Actions: Make sure that no pages you actually want to appear in the search results have accidentally been included in the Excluded category.
Indexation issues can get complicated, but in general, you want to make sure that:
- Google indexes all the pages on your site you want to appear in the search results.
- Google doesn’t index the pages you want to keep out of the search results.
- You address any errors or warnings Google flags.
For more information on the Index Coverage report — and to find out how to fix specific errors – the Google documentation is helpful.
Using the Removals Tool
The Removals Tool can be useful in certain situations if you want pages on your site to be temporarily removed from the search results. It’s not possible to permanently remove URLs using this tool, since Removals requests only last about six months.

There are three types of removal requests:
Temporary Removal — Great for taking individual or entire categories of URLs out of Google search results immediately. You can also clear any cached page information still appearing in the search results.
Outdated Content — Shows instances of people reporting outdated content on your site, as well as pages missing content that’s been indexed.
Safe Search — Shows instances of people reporting sexually explicit content on your pages.
Use the Removals tool when you want something to disappear from search results right away, or if you want to clear and refresh the meta description in the search results for a particular page.
If you want any content permanently removed from the search results, you’ll need to use noindex meta tags, or make sure your server returns 410 (gone) or 401 (page not found).
Using the Enhancements Report
Which enhancements appear in Google Search Console’s left-hand navigation will be largely dependent on your site’s structured data or lack thereof.
That being said, you may see data on two key enhancements that aren’t directly related to your site’s structured data.
Speed
One of the foundations of a good user experience, and thus SEO, is having fast-loading pages. If pages take too long to load, people will quickly leave your site in search of pages (and content) they can actually use.
The Speed report shows you both mobile and desktop page speed performance. Each of your pages will be categorized as slow, moderate, or fast.

Slow-loading pages on your site need to be addressed. If they aren’t in the “moderate” or “fast” categories on both desktop and mobile, consider looking into Google’s recommendations about how to improve your page speed and taking action.
Mobile Usability
Another key principle of creating a quality user experience is having pages that are mobile-friendly, i.e. responsive. That’s because so many people are using mobile devices to browse websites like yours. If your pages aren’t mobile-friendly, Google will take notice and send people elsewhere instead.
The Mobile usability tool in Search Console allows you to see how many pages on your site are mobile-friendly, how many are not, and how each individual page is categorized.
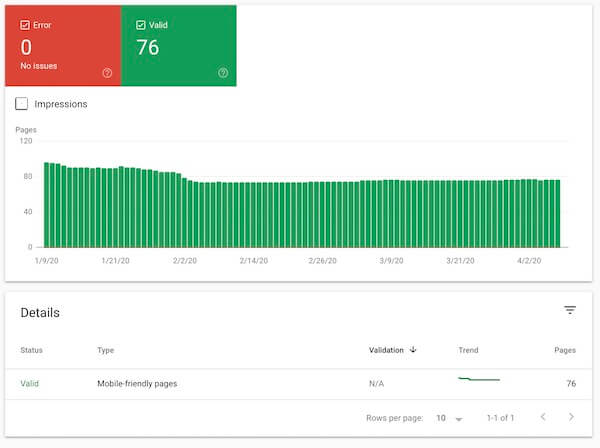
Make sure that all the pages on your site are mobile-friendly, and that you address any that aren’t. Google provides some guidelines on how to prioritize and fix specific issues.
Google also offers great documentation on dealing with enhancement issues. All you have to do is click on a particular type of enhancement in the Details table, then click LEARN MORE to access documentation related to that enhancement.
AMP & Rich Results
Two other and more common enhancements in Search Console reports are accelerated mobile pages and rich results. While we aren’t going to go into detail here (since not everyone will have them), it’s still worth learning how to leverage the reports if your site is using those enhancements.
Using the Links Report
Internal and external links are important in SEO. Internal links help Google understand the relative importance of your various pages. External links (links on other sites that direct users to yours) tell Google if your website is authoritative and trustworthy. A solid internal link architecture and lots of high-quality external links pointing to your site are both critical for successful SEO.
The Links Report in Google Search Console is the best free way to inform your SEO link building strategy. That’s because this report shows you:
- Which sites are linking to you the most,
- Which pages they’re linking to,
- The text most frequently used in those external links, and
- Which pages on your site have the most internal links pointing to them.
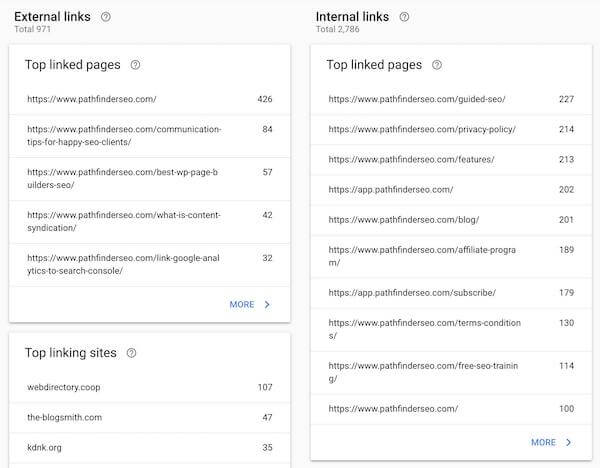
Use this report to make sure that the most important pages on your site have the most internal links pointing to them and the least important pages have the least internal links pointing to them. Link architecture set up in the opposite way will send Google mixed signals about what pages are important on your site.
Also, use this report to analyze the effectiveness of your link building strategy and to identify new opportunities that you are not yet taking advantage of.
Pay Attention to Manual Actions and Security
Google is able to tell a lot about your site just by crawling it. On occasion, Google will take issue with something.
When this happens, a human reviewer will look at your site to see what’s going on. If that reviewer identifies something that is not in line with Google’s webmaster quality guidelines, you will be notified in the Manual actions section of Google Search Console. You will be told what the issue is, and given advice on how to fix it. If you do not fix the issue, your site may be demoted — or omitted from the rankings altogether.
Using the Security Reports in Google Search Console
When Google is crawling your site, there are three types of security issues that it can easily identify:
- If your site has malware or undesired software on it,
- If it’s been hacked,
- If it’s experiencing a social engineering attack.
Take action immediately using Google’s documentation if your site is experiencing any of these issues.
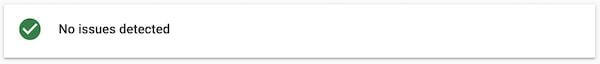
If you’re playing by the rules and nobody is attacking your site, you should never see anything other than “No issues detected” in the Manual Actions and Security sections of Google Search Console.
Getting Help & Documentation in Google Search Console
You should now have a solid idea of what the various reports and tools in Google Search Console can help you accomplish. However, this is just an intro to the platform; there is much more that we just can’t cover here.
If you have any questions about a particular report, simply click on the question mark icon when looking at that report and relevant documentation will appear.
Also, don’t be afraid to click on the little question mark icons or the LEARN MORE links when you see them.
Lastly (and it may seem like a no brainer), if you don’t see the answer you’re looking for in Google’s documentation, do a Google search. There are millions of people using Google Search Console, asking questions about it, and getting answers from other users. A Google search is often the quickest, most direct way to get moving in the right direction.
Get Google Search Console Training
If you’re thirsty for more Google Search Console training, Google has a great video series dedicated to teaching you all things GSC.
If you want help with your SEO strategy as it relates to Google Search Console and beyond, learn how the team at Pathfinder SEO can help you take a guided approach to improve your site’s performance in search results.